FAQ
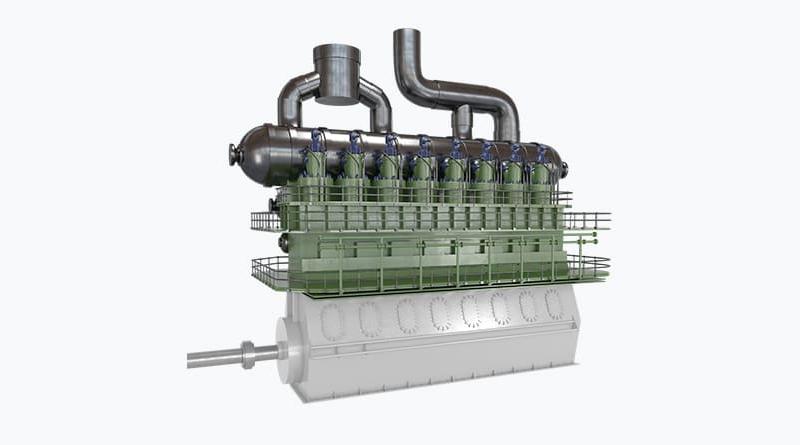
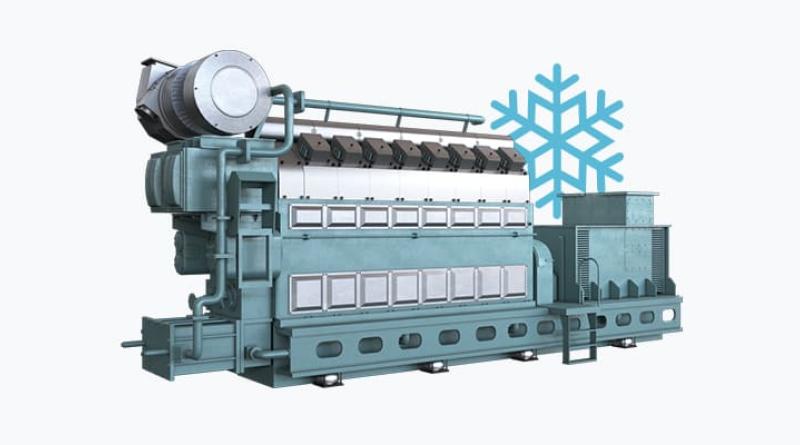
Power Generation Industry, Power Plant, Powerhouse
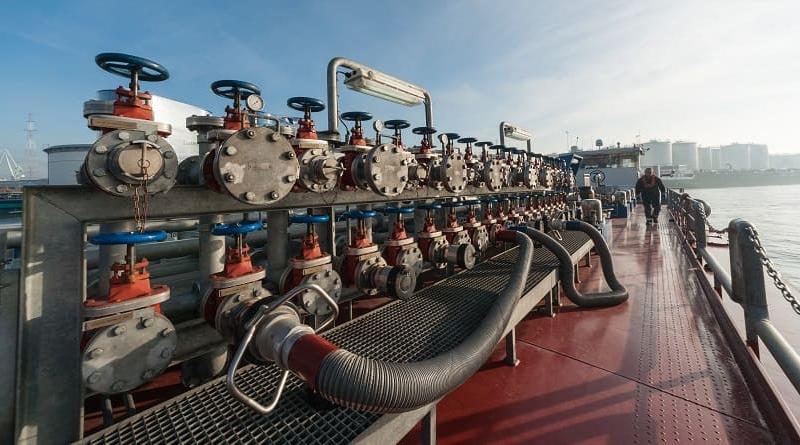
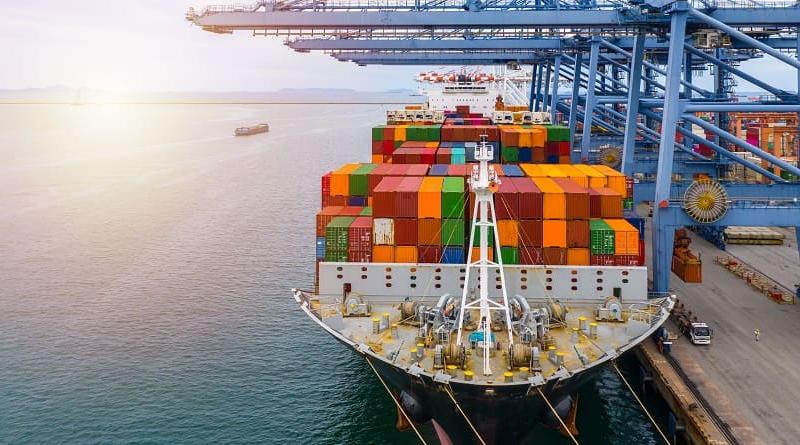
A power plant or powerhouse, and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power.
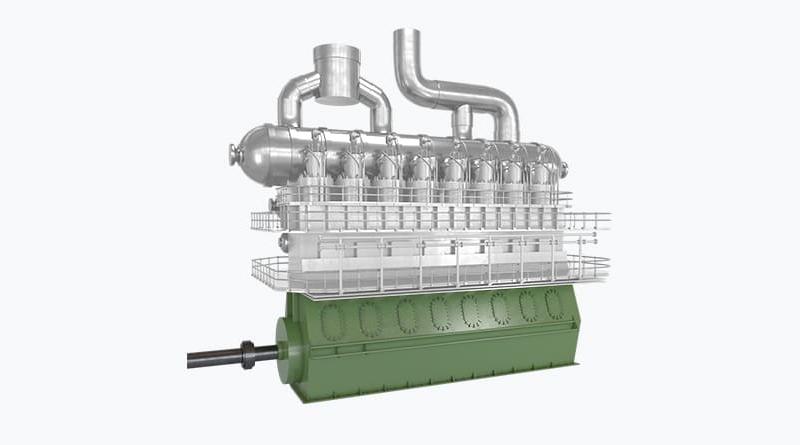
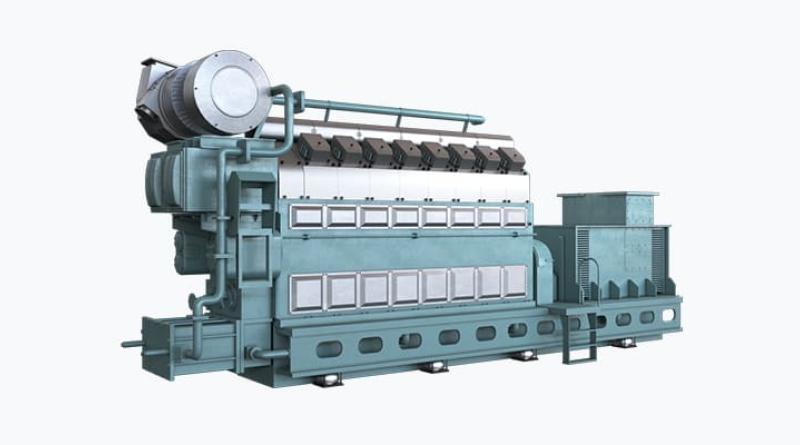
Most power plants contain one or more generators, a rotating machine that converts mechanical power into electrical power. The relative motion between a magnetic field and a conductor creates an electrical current. The energy source harnessed to turn the generator varies widely.
Most power stations in the world burn fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas to generate electricity. Fossil-fuel power stations may also use a steam turbine generator or in the case of natural gas-fired plants may use a combustion turbine.
Steam turbine plants use the dynamic pressure generated by expanding steam to turn the blades of a turbine. Almost all large non-hydro plants use this system. About 90 percent of all-electric power produced in the world is through the use of steam turbines.
Gas turbine plants use the dynamic pressure from flowing gases (air and combustion products) to directly operate the turbine. Natural-gas fuelled (and oil-fueled) combustion turbine plants can start rapidly and so are used to supply "peak" energy during periods of high demand.
Combined cycle plants have both a gas turbine fired by natural gas and a steam boiler and steam turbine which use the hot exhaust gas from the gas turbine to produce electricity. This greatly increases the overall efficiency of the plant, and many new baseload power plants are combined cycle plants fired by natural gas.